Other tongue lesions
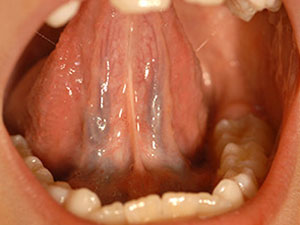
Ankyloglossia
Congenital too short, thick lingual frenulum, which connects the underside of the tongue to the floor of the mouth. A surgical solution is only necessary, if the function of the tongue is restricted. Occasionally ankyloglossia occurs together with ectodermal dysplasia.
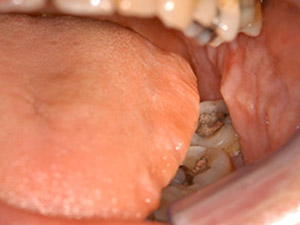
Lateral lingual tonsils
It is lymphatic tissue located symmetric on the back, lateral edges of the tongue and is often not easy to be distinguished from hypertrophic foliata papillae. The surface appears furrowed and red. The palpable lesion is soft. If it comes to a tonsillitis it can be painful.
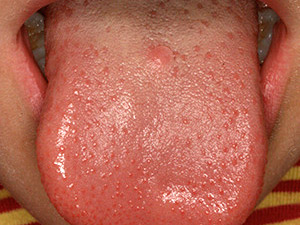
Heterotopic vallata papillae
Heterotopic location of the vallata papillae, mostly on the dorsal surface of the tongue, sometimes also on the palatine arch can upset a patient even though it is neither painful nor does it necessitate a therapeutic intervention.
Lateral tongue impressions
Disproportion of the size of the tongue and the jaw or parafunctions like tongue thrust can lead to lateral tongue impressions
Thyroid glands hypertrophy
The so called lingual goiter manifests itself as a knotty, highly vascularized excess tissue on the root of the tongue. Surgical intervention is only needed if the function is restricted.
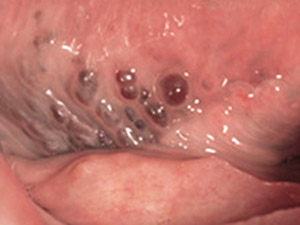
Lingual varicosities
Prominent veins on the bottom side of the tongue can occur more frequently with increasing age. Multiple venectasias can lead to the image of the so called 'caviar-tongue'. Therapeutic intervention is not indicated. back
Congenital too short, thick lingual frenulum, which connects the underside of the tongue to the floor of the mouth. A surgical solution is only necessary, if the function of the tongue is restricted. Occasionally ankyloglossia occurs together with ectodermal dysplasia.
Lateral lingual tonsils
It is lymphatic tissue located symmetric on the back, lateral edges of the tongue and is often not easy to be distinguished from hypertrophic foliata papillae. The surface appears furrowed and red. The palpable lesion is soft. If it comes to a tonsillitis it can be painful.
Heterotopic vallata papillae
Heterotopic location of the vallata papillae, mostly on the dorsal surface of the tongue, sometimes also on the palatine arch can upset a patient even though it is neither painful nor does it necessitate a therapeutic intervention.
Lateral tongue impressions
Disproportion of the size of the tongue and the jaw or parafunctions like tongue thrust can lead to lateral tongue impressions
Thyroid glands hypertrophy
The so called lingual goiter manifests itself as a knotty, highly vascularized excess tissue on the root of the tongue. Surgical intervention is only needed if the function is restricted.
Lingual varicosities
Prominent veins on the bottom side of the tongue can occur more frequently with increasing age. Multiple venectasias can lead to the image of the so called 'caviar-tongue'. Therapeutic intervention is not indicated. back