Mononucleosis
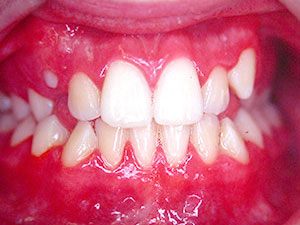
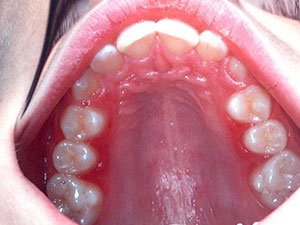
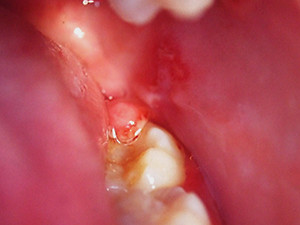
Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) is the causative agent of the infectious mononucleosis or the so-called 'kissing disease'. Primary infection occurs mostly in adolescence. Symptoms are severe tiredness, sore throat, adenopathy and sometimes spleno- or hepatomegaly. Typical oral manifestations are palatal petechiae, especially located at the transition of the soft to the hard palate and exsudative pharyngitis and tonsillitis. The tonsils are covered with pseudomembranous, white-yellow coatings. Treatment lies in adequate hydration, analgesics and antipyretics. Once the acute phase has passed (after some days till weeks), myalgias and fatigue can persist over a few months. A reactivation of the virus is possible.
Pathogen: Epstein-Barr Virus
Transmission path: droplet infection
Incubation time: 8-21 days Contagiousness: 1-3 weeks
Prodromal symptoms: -
Symptoms: generalised lmyphadenitis, severe tiredness, sore throat, adenopathy, exsudative pharyngitis and tonsillitis
Treatment: symptomatically
Complications: seldom back
Pathogen: Epstein-Barr Virus
Transmission path: droplet infection
Incubation time: 8-21 days Contagiousness: 1-3 weeks
Prodromal symptoms: -
Symptoms: generalised lmyphadenitis, severe tiredness, sore throat, adenopathy, exsudative pharyngitis and tonsillitis
Treatment: symptomatically
Complications: seldom back