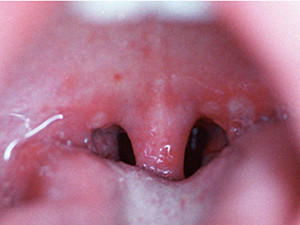
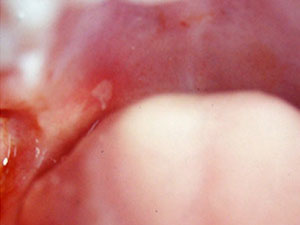
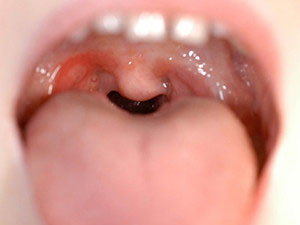
Angina herpetica
Herpangina (zachorsky) is associated with various enteroviruses, especially with Coxsackie virus group A. It is an acute infection which occurs mostly within the first two years after birth and more frequently in the summer months. It starts with sore throat, dysphagia, fever and headache and within the following 24-48 hours diffuse erythema and vesicular eruption of the oral mucosa occur. The lesions are characteristically located on the soft palate, the oropharynx and rarely involve the buccal mucosa or the tongue. The vesicles are small, multitudinous and leave painful, plain ulcers after rupture with a red halo. Symptomatic treatment may be induced.
Pathogen: various enterovirus serotypes, coxsackievirus A5
Transmission path: droplet infection or via the 'fecal-oral route' Incubation time: 2-6 days
Contagiousness: a few days before the lesions appear until they have healed
Prodromal symptoms: rapidly increasing high fever, diffuse erythema on the soft palate
Symptoms: painful vesicular eruption of the oral mucosa, fever, nausea, headache, sore throat
Treatment: symptomatically
Complications: bacterial superinfection back
Pathogen: various enterovirus serotypes, coxsackievirus A5
Transmission path: droplet infection or via the 'fecal-oral route' Incubation time: 2-6 days
Contagiousness: a few days before the lesions appear until they have healed
Prodromal symptoms: rapidly increasing high fever, diffuse erythema on the soft palate
Symptoms: painful vesicular eruption of the oral mucosa, fever, nausea, headache, sore throat
Treatment: symptomatically
Complications: bacterial superinfection back