Oral candidiasis
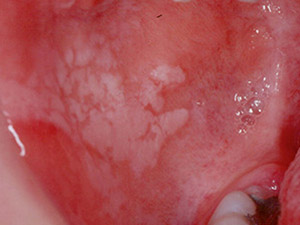
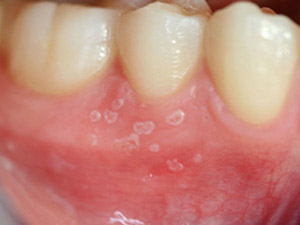
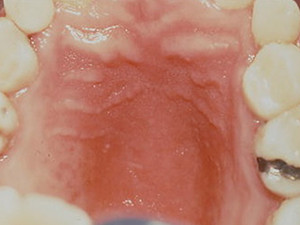
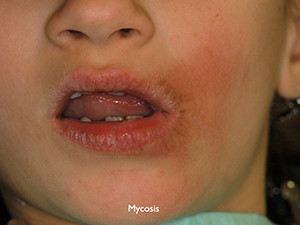
Oral candidiasis is a general term for infections with blastomycetes of the genus candida, mostly candida albicans. The infection manifests itself in various forms but primarily as 'pseudomembranous' candidiasis or, more commonly called, 'oral thrush'. It usually shows asymptomatic, confluent white plaques which can be wiped off. The underlying mucous membrane appears erythematous. The plaques are possible to occur everywhere on the oral mucosa and consist of fungal hyphae, fibrin and desquamated epithelial cells. Candida species belong to the normal oral flora but may lead to candidiasis predominantly in individuals who are immunodeficient, take pharmalogical agents, in children, in denture wearers or people with nutritional deficiencies. The treatment lies in the correction of the underlying predisposing factor and anti-fungal agents may are indicated.
back