Scarlet fever
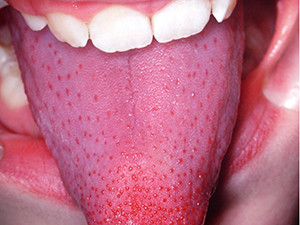
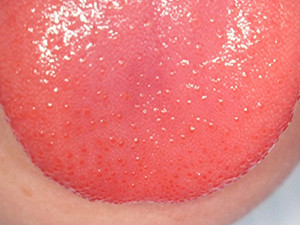
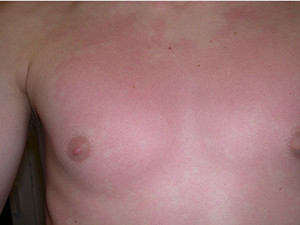
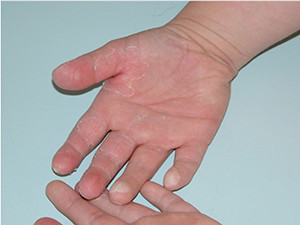
Scarlet fever is an acute infectious disease with a typical exanthema and tonsillitis, due to exotoxins of beta-haemolytic streptococci and is, therefore, no viral disease. After an incubation period of 2-8 days, prodromal symptoms like tonsillitis, high grade fever or reduced general condition show up. After 2 days, perioral, a butterfly like rush is a further typical sign, giving the erythematous exanthema of the skin a sand paper feel (which in a further process starts to desquamate). Intraoral, the tonsils are reddened and purulent, the tongue is first white coated and after 4-5 days it becomes smooth, bright red with swollen papillae and strongly resembles the so-called 'raspberry tongue'.
Treatment with antibiotics is useful and can prevent complications.
Pathogen: Group A beta-hemolytic Streptococci (no virus!)
Transmission path: droplet infection, seldom smear infection
Incubation time: 2-8 days
Contagiousness: until 24 hours after the first dose antibiotic
Prodromal symptoms: sore throat, high grade fever, reduced general condition, furred tongue
Symptoms: erythematous exanthema of the skin, raspberry tongue, tonsillitis, pharyngitis
Treatment: Penicilline G/ antibiotics
Complications: otitis media, myocarditis, purulent lymphadenitis, acute rheumatic fever etc. back
Treatment with antibiotics is useful and can prevent complications.
Pathogen: Group A beta-hemolytic Streptococci (no virus!)
Transmission path: droplet infection, seldom smear infection
Incubation time: 2-8 days
Contagiousness: until 24 hours after the first dose antibiotic
Prodromal symptoms: sore throat, high grade fever, reduced general condition, furred tongue
Symptoms: erythematous exanthema of the skin, raspberry tongue, tonsillitis, pharyngitis
Treatment: Penicilline G/ antibiotics
Complications: otitis media, myocarditis, purulent lymphadenitis, acute rheumatic fever etc. back