Impetigo contagiosa/ school sores
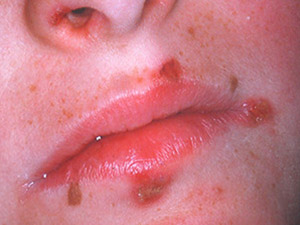
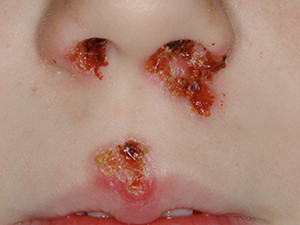
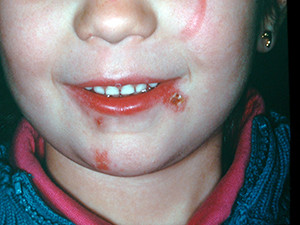
Impetigo contagiosa is a highly contagious infection of the skin caused by group A beta-hemolytic Streptococci and Stphylococcus aureus.
It is the most common pyoderma in children, transmitted by smear infection. Of the two existing types, bullous and nonbullous impetigo, the nonbullous type is far more common, however, combined versions are possible.
The typical skin manifestation of the nonbullous impetigo starts with pimple-like lesions surrounded by reddened skin predominantly located on face, arms and legs. After a few days the lesions fill with purulence, and after they have burst, they build thick honey-yellow crusts which mostly create an itching sensation. The bullous type of impetigo shows bigger lesions, 2-5 cm bullae, which are filled with serous fluid.
The treatment options are oral or topic fusidic acid, mupirocin or antibiotics. Complications like glomerulonephritis are possible but rare. back
It is the most common pyoderma in children, transmitted by smear infection. Of the two existing types, bullous and nonbullous impetigo, the nonbullous type is far more common, however, combined versions are possible.
The typical skin manifestation of the nonbullous impetigo starts with pimple-like lesions surrounded by reddened skin predominantly located on face, arms and legs. After a few days the lesions fill with purulence, and after they have burst, they build thick honey-yellow crusts which mostly create an itching sensation. The bullous type of impetigo shows bigger lesions, 2-5 cm bullae, which are filled with serous fluid.
The treatment options are oral or topic fusidic acid, mupirocin or antibiotics. Complications like glomerulonephritis are possible but rare. back