Erythema infectiosum
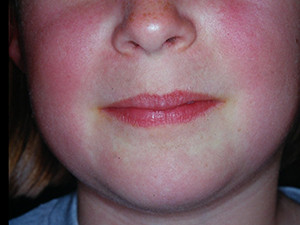
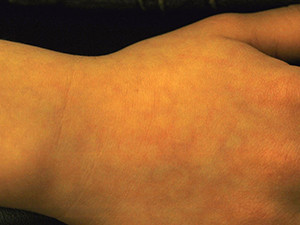
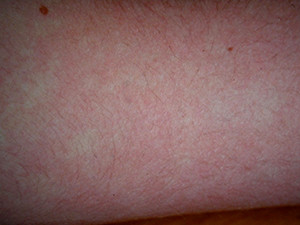
The 'fifth disease' or also called 'slap-cheek disease' is a viral infection with the parvovirus B19. It mostly occurs in children aged between 6 and 15 years. After an incubation period of 7-14 days, a general feeling of illness and fever may come up accompanied by a butterfly-shaped erythema on the facial skin and a perioral paleness, later on the extremities and the trunk ring and girland-like, partly itchy erythema. From the moment when the rush appears, the virus is no longer infectious. The fifth disease shows no oral manifestation. It heals spontaneously within 2 weeks and usually needs only supportive treatment.
Pathogen: human parvovirus B19
Transmission path: droplet infection Incubation time: 7-14 days
Contagiousness: 10-14 days until the exanthema appears
Prodromal symptoms: -
Symptoms: butterfly-like erythema on the facial skin, later ring and garland-like erythema on extremities and trunk
Treatment: symptomatically
Complications: arthritides in adults, extremely rarely bacterial superinfections back
Pathogen: human parvovirus B19
Transmission path: droplet infection Incubation time: 7-14 days
Contagiousness: 10-14 days until the exanthema appears
Prodromal symptoms: -
Symptoms: butterfly-like erythema on the facial skin, later ring and garland-like erythema on extremities and trunk
Treatment: symptomatically
Complications: arthritides in adults, extremely rarely bacterial superinfections back