Type IV: delayed hypersensitivity reactions
The so-called 'delayed hypersensitivity reactions'? occurs due to a linking between a per se non immunogenic allergen and a (body's own) protein which is able to induce an immune reaction (T-cell-B-cell cooperation). The then produced cytokines and inflammatory mediators lead to an increased activity of macrophages respectively to a phototoxic reaction.
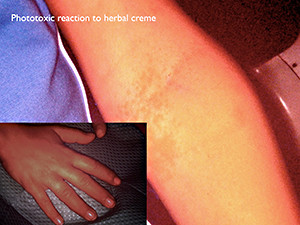
Normally, clinical manifestations like erythema, papules and/or blisters occur 2 to 7 days after the cutaneous drug exposure. Typical examples are contact dermatitis, Steven-Johnson syndrome, chronic asthma or chronic allergic rhinitis. back
Normally, clinical manifestations like erythema, papules and/or blisters occur 2 to 7 days after the cutaneous drug exposure. Typical examples are contact dermatitis, Steven-Johnson syndrome, chronic asthma or chronic allergic rhinitis. back