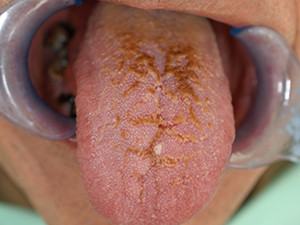
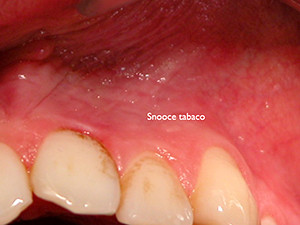
Smoker's melanosis
Tobacco smoke contains noxious agents which can cause an immunological response of the melanocytes which, in turn, increase their production of melanin. As a result brown-black lesions show up which are mainly located on the anterior labial gingiva, followed by the buccal mucosa. This phenomenon occurs in about 20per cent of all smokers and is likely to fade out after smoking cessation inside of three years.
back