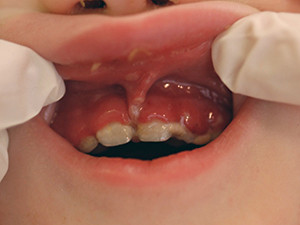
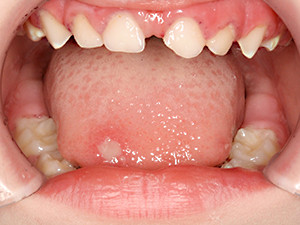
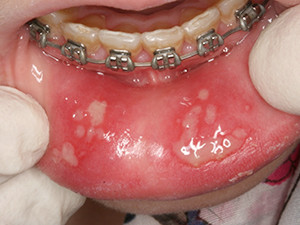
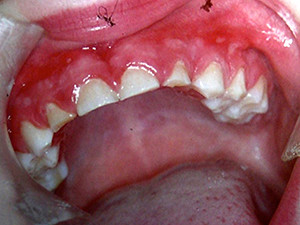
Gingivostomatitis herpetica
Herpetic stomatitis expresses the initial manifestation of the herpes simplex virus type 1 and 2. The lesion appears normally just once and mostly during childhood. After an incubation period of 2-7 days, general symptoms like fever, emesis and fatigue occur in combination with swelling of the palate, the gingiva and the regional submandibular lymph nodes. The numerous vesicles that follow rupture rapidly and turn into painful aphthous-like ulcers, typically located on the anterior part of the mouth. Bad breath and sialorrhea are characteristic. The lesions heal within 10-14 days. Symptomatic treatment is induced, virostatic agents may be conducive if used at an early stage. Reactivation of the virus causes the common herpes labialis.
Pathogen: Herpes Simplex Virus Type 1 or 2
Transmission path: droplet infection, contact with lesions
Incubation time: 2-7 days
Contagiousness: until the lesion crust over
Prodromal symptoms: fever, fatigue, muscle aches, cervical and submandibular lymphadenopathy
Symptoms: sialorrhea, foeter ex ore, aphthoid lesions/ ulcerations
Treatment: symptomatically
Complications: bacterial superinfections, eczema herpeticum, herpes simplex encephalitis back
Pathogen: Herpes Simplex Virus Type 1 or 2
Transmission path: droplet infection, contact with lesions
Incubation time: 2-7 days
Contagiousness: until the lesion crust over
Prodromal symptoms: fever, fatigue, muscle aches, cervical and submandibular lymphadenopathy
Symptoms: sialorrhea, foeter ex ore, aphthoid lesions/ ulcerations
Treatment: symptomatically
Complications: bacterial superinfections, eczema herpeticum, herpes simplex encephalitis back