HIV infection
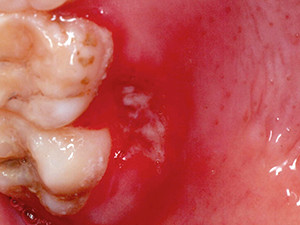
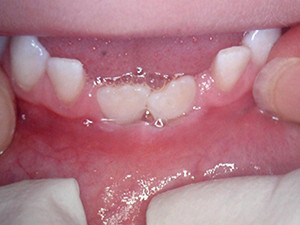
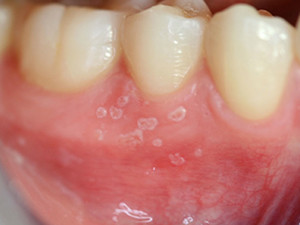
HIV infected patients often develop oral lesions. The most typical oral manifestations are candidosis, angular cheilitis, oral hairy leukoplakia, linear gingival erythema, Kaposi's sarkoma, necrotizing ulcerative gingivitis or periodontitis and non-Hodgkin lymphoma. Atypical ulcers, salivary glands diseases or other viral infections are additionally possible symptoms. The lesions can appear as solitary or combined disorders. In most cases, the tongue is involved. The wide range of oral manifestation of the virus can provide valuable prognostic and diagnostic information.
Pathogen: HIV virus Transmission path: blood or mucous membrane contact with infected blood, sperm, vaginal fluids and other body fluids (except saliva)
Incubation time: 2-6 weeks
Contagiousness: depends on the concentration of the virus in the body fluids
Prodromal symptoms: -
Symptoms: mononucleosis-like symptoms, persisting efflorescences, fungal diseases, recurring pneumonal infections
Treatment: HIV-pharmaceuticals
Complications: AIDS (acquired immunodeficiency syndrome) back
Pathogen: HIV virus Transmission path: blood or mucous membrane contact with infected blood, sperm, vaginal fluids and other body fluids (except saliva)
Incubation time: 2-6 weeks
Contagiousness: depends on the concentration of the virus in the body fluids
Prodromal symptoms: -
Symptoms: mononucleosis-like symptoms, persisting efflorescences, fungal diseases, recurring pneumonal infections
Treatment: HIV-pharmaceuticals
Complications: AIDS (acquired immunodeficiency syndrome) back